eGFR Calculator for Doctors: Mastering Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate in Evidence-Based Medicine
- Akhila Kosuru
- Nov 29, 2025
- 3 min read
Updated: Dec 4, 2025
In clinical practice, accurately assessing kidney function is foundational for evidence-based medicine, particularly when managing chronic kidney disease (CKD), dosing nephrotoxic drugs, and staging renal impairment. The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) serves as the gold standard surrogate for measured GFR, derived from serum creatinine levels Kidney, GFR, Evidence, eGFR, Doctors, Chronic Kidney Disease adjusted for age, sex, and race. For doctors navigating complex patient cases, tools like the eGFR calculator streamline this process, enabling precise diagnostics without invasive testing. This article explores eGFR in depth, highlighting its clinical utility, calculation nuances, and integration with platforms like AstraAI from Augsidius Health Technologies.
What is eGFR and Why It Matters in Daily Practice?
eGFR quantifies the kidneys' filtration capacity, expressed in mL/min/1.73 m², reflecting the rate at which blood is cleared of waste. Unlike raw serum creatinine, which varies with muscle mass and diet, eGFR incorporates demographic factors for superior accuracy. In evidence-based medicine, routine eGFR reporting by labs empowers physicians to detect CKD early, often before symptoms manifest, and reducing progression to end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
For Indian doctors, where diabetes and hypertension drive 40-50% of CKD cases, eGFR guides risk stratification. Values ≥90 indicate normal function, 60-89 suggest mild decline (monitor closely), 30-59 signal moderate CKD, 15-29 severe impairment, and <15 kidney failure requiring dialysis or transplant. AstraAI's suite of hundreds of calculators, including advanced eGFR tools, automates this for busy clinicians, pulling from validated formulas to support research and patient care.
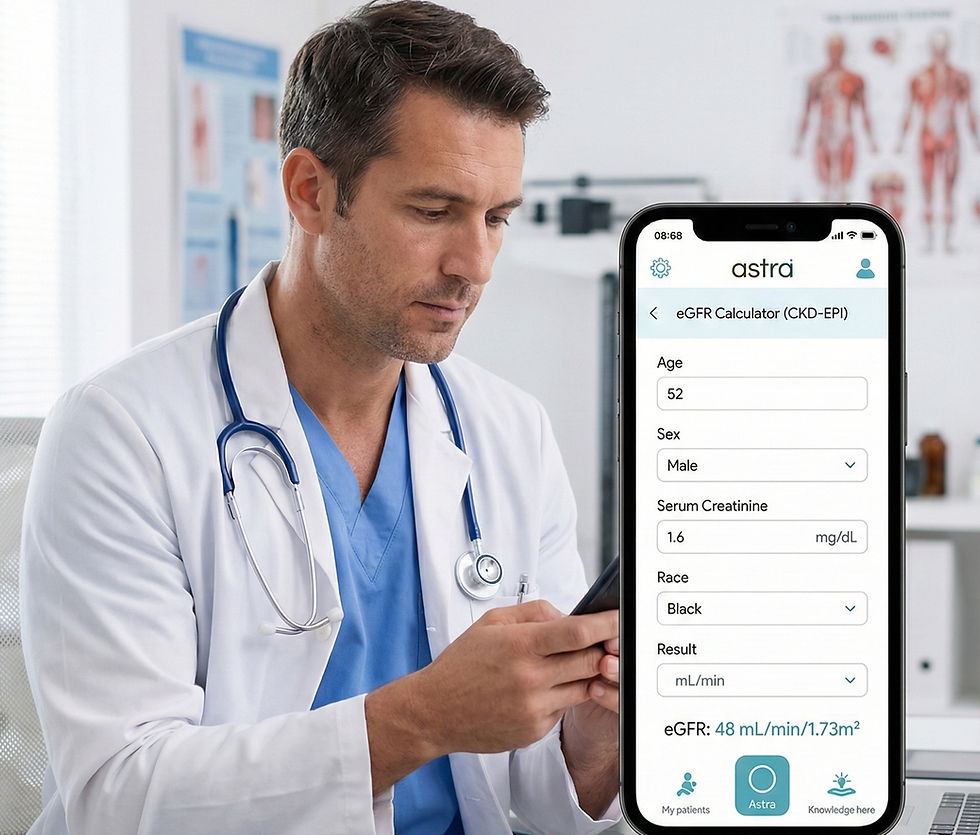
Evolution of eGFR Equations: From MDRD to CKD-EPI
Early equations like the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula advanced kidney assessment but underestimated GFR at higher levels (>60 mL/min/1.73 m²), leading to overdiagnosis of CKD stage 3. This bias affected prevalence estimates, inflating U.S. CKD rates to 13.1% in NHANES data.
The CKD-EPI equation, developed by the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration, addressed these limitations through rigorous cross-sectional analysis of over 8,000 participants with measured GFR via iothalamate clearance. Credits to Levey et al. (2009) for pioneering this in Annals of Internal Medicine, where pooled datasets from 10 studies refined coefficients for log-transformed creatinine, age, sex, and race. Validation in 3,896 external cases showed CKD-EPI outperforming MDRD: median bias of 2.5 vs. 5.5 mL/min/1.73 m², precision (IQR 16.6 vs. 18.3), and accuracy (84.1% vs. 80.6% within 30% of measured GFR).
Chronic Kidney Disease - CKD-EPI Formula (Paraphrased for Clinical Use) :
GFR = 141 × min(Scr/κ, 1)^α × max(Scr/κ, 1)^−1.209 × 0.993^Age × (1.018 if female) × (1.159 if Black), where Scr is serum creatinine (mg/dL), κ=0.7 (female)/0.9 (male), α=−0.329 (female)/−0.411 (male).This shift reduced NHANES CKD prevalence to 11.5%, minimizing false positives in healthy populations.
AstraAI's eGFR Calculator: Empowering Doctors' Research Journey
At Augsidius Health, AstraAI embodies evidence-based medicine by embedding CKD-EPI and MDRD calculators, among hundreds for cardiology, endocrinology, and more; directly into doctors' workflows. Developed referencing Levey et al.'s landmark study, AstraAI recalibrates creatinine to standardized assays (e.g., Roche enzymatic method), ensuring precision across diverse demographics, including Indian patients with varying muscle mass.
Key features for physicians:
Instant Calculations: Input creatinine, age, sex, race; get staged CKD reports with confidence intervals.
Research Integration: Export data for publications, trials, or longitudinal tracking, aligning with ICMR guidelines.
Bias Mitigation: Race-neutral options per 2021 KDIGO updates, plus cystatin C integration for high-risk cases (e.g., elderly, amputees).
Evidence-Based Alerts: Flags inaccuracies from extremes (e.g., BMI >30, vegetarians) and suggests measured GFR via iohexol if needed.
In pediatrics or oncology, eGFR aids chemotherapy dosing and hypertension management, cutting errors by 20-30% per validation studies.
Clinical Interpretation of eGFR and Limitations in Evidence-Based Practice
Interpret eGFR alongside albuminuria (ACR ≥30 mg/g) for full CKD diagnosis per KDIGO. Trends over 3-6 months trump single readings, as acute changes signal AKI. In evidence-based medicine, combine with biomarkers like NGAL for prognosis.
Limitations persist: CKD-EPI assumes steady-state creatinine, falters in cirrhosis, malnutrition, or extremes of age/muscle. For accuracy <30% error, confirm with measured GFR in donors or transplants. Indian contexts demand cystatin C-adjusted models due to dietary creatinine variations.
eGFR Range (mL/min/1.73 m²) | CKD Stage | Management Focus |
≥90 | Normal | Risk factor control |
60-89 | G1/G2 | BP <130/80, SGLT2i |
30-59 | G3 | ACEi/ARB, nephrology ref |
15-29 | G4 | Dialysis prep |
<15 | G5 | Transplant evaluation |
Optimizing Kidney Care with Technology and Evidence
Clinical Calculators like eGFR through AstraAI, transform evidence-based medicine from theory to practice, enabling Indian doctors to publish high-impact research while optimizing clinical practice. Regular screening halves ESRD risk; integrate AstraAI today for seamless CKD-EPI computations. Future updates may incorporate AI-driven cystatin C fusions, per ongoing trials.
To integrate evidence based medicine into your daily kidney care decisions, start using AstraAI’s eGFR calculator today and let us know your feedback in the comments below.



Comments